High pressure pump
High pressure pumps are one of the main components of any RO system. These pumps should provide a uniform flow to the RO elements. The design of these pumps should be such that it provides the desired flow rate at the desired pressure of the system for different working conditions of the membrane life.
High pressure pump energy consumption is one of the cost items on the RO system. Therefore, the high energy efficiency of these pumps is one of the basic factors in the economic evaluation of the system.
Centrifugal pumps are often used in RO systems with a pressure lower than Psig400. In these pumps, when the water reaches the outside of the impeller, it has the highest speed, then when the water leaves the pump, the speed becomes pressure.
Centrifugal pumps are capable of producing continuous and uniform pressure and flow. But in some cases, in order to create the required high pressure in the RO system, a pump with a large impeller in terms of dimensions or a standard impeller with a very high speed is needed. In such cases, multi-stage centrifugal pumps are used. In multi-stage centrifugal pumps, a number of impellers are connected in series in order to increase the pressure. A bearing collects water from the previous blade and feeds it to the next blade.
All multi-stage centrifugal pumps have higher energy efficiency than high-speed single-stage centrifugal pumps. Each multi-stage pump vane increases the pressure of the water passing through it by up to 30 Psi. The tension force applied to the water is reduced and as a result less energy is wasted by friction and turbulence of the flow.
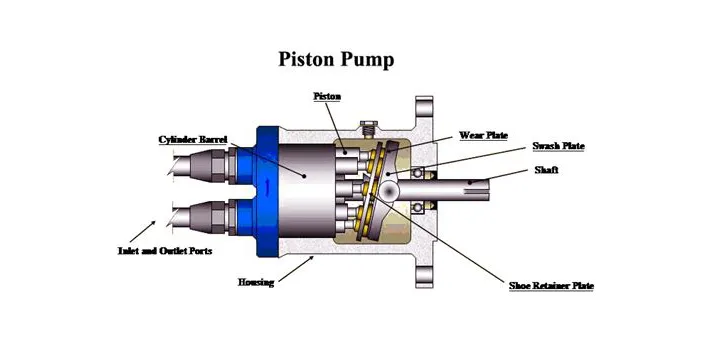
In some cases, piston pumps are used to provide the high pressure required in the RO system. The big disadvantage of these pumps is the fluctuations in the speed of the flow coming out of them. These speed fluctuations are one of the causes of the telescopic phenomenon.
During this phenomenon, the different layers of the membrane element are pulled out and the element takes the shape of a telescope, which is likely to cause mechanical damage to the membrane element. Therefore, when the RO system is in service, it is a good idea to use dampening devices downstream of the piston pump.
Pump curve
The output pressure of a high pressure pump used in RO systems is determined by the curve of that pump. Pump flow rate is equal to the sum of product water, waste water and recycle flows.
The pump curve is used to select the most suitable pump to provide the required flow and pressure. As shown in Figure 1, if a flow rate of 140 gpm with a pressure of at least 200 psig is desired, the pump model will be type 12509.
For this flow rate, the pump pressure will be 210 psig. Since the water entering the pump is pressurized, the actual pump pressure will be more than 210 psig. For example, city water pressure may be 70 psig, which drops to 55 psig after sand filters and cartridge filters upstream of the RO, and the actual pressure at the outlet of the high pressure pump in this example will be 265 psig.
In choosing a high pressure pump, the pump should be designed in such a way that according to the diagram below, it has the maximum efficiency. The power of the pump should be considered in such a way that the pump is never able to pass a flow greater than what is designed. The maximum power is obtained by multiplying the power by the reliability factor.
If there is a possibility of failure in a path or accidental opening of a valve, which causes the long-term operation of the electric motor of the pump above its selected maximum power, a larger electric motor should be used. The power that the electric motor actually uses is called breaking power.
Nowadays, for pure water applications, an oversize pump is usually not necessary, perhaps the result is energy waste. The design of a pump must be precisely sized to provide the desired pressure and flow. Expecting a slight increase in the system in the future is an exception to this rule.
If there is a possibility of increasing the capacity in the future, it should be possible to build an RO row independently. This row can be installed on an existing RO frame provided that the frame originally made is sized for the latter. If one of the RO systems is not in service for repairs, the other must be able to supply the required water.
Electric motor efficiency
The efficiency of the electric motor is a factor that must be considered. Some electric motors have low efficiency like 92%. This value is comparable with the efficiency of 98% to 99% for electric motors designed for high efficiency. Higher efficiency can save energy.
In some cases, high-pressure floating pumps that are installed on tubes under horizontal pressure are used in RO systems. Although these pumps have become popular due to their energy efficiency, their floating electric motors are less efficient than standard air-cooled motors. The only advantage of these pumps is their low noise and floating.